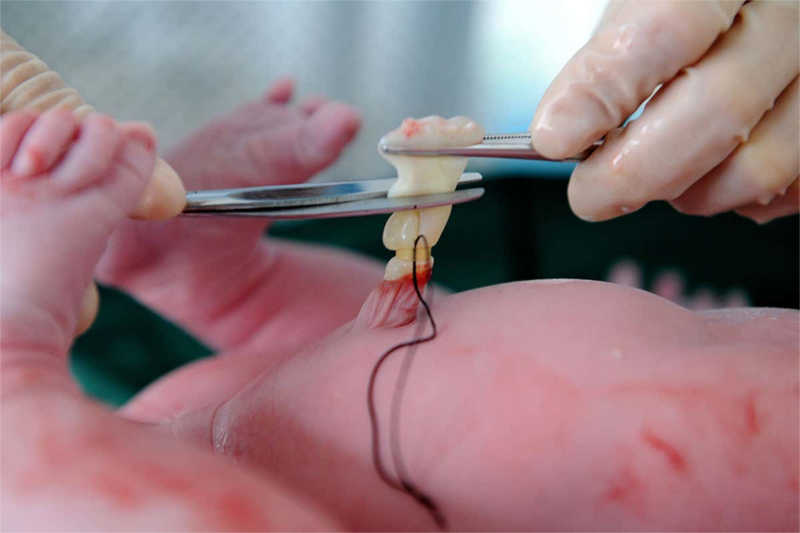
Cord Blood Banking
Before we go into the details of Cord Blood Banking, its pros & cons, and whether you should go for it, lets understand what is cord blood.
What is Cord Blood?
In simple language “Cord Blood” is the blood that is left in the umbilical cord and placenta after delivery of a baby. This blood contains special cells called Hematopoietic Stem Cells. These cells can be used to treat some types of diseases which may come up in the baby.
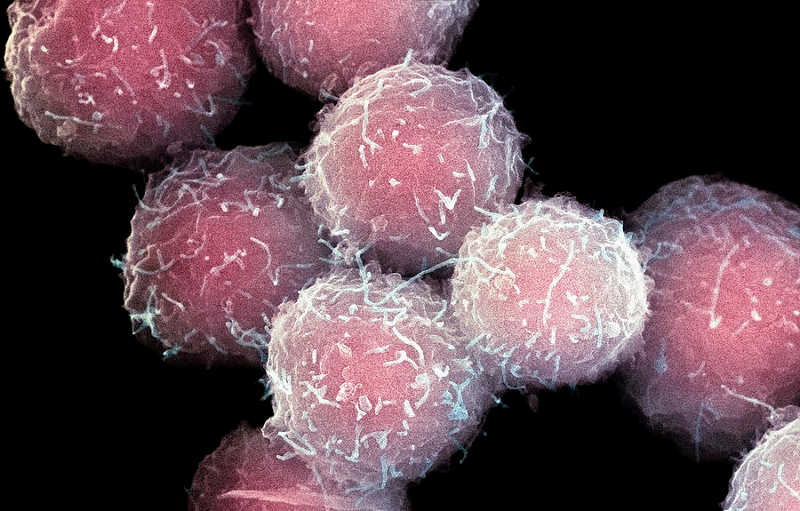
Let us explain stem cells further. We know that cells in our body can copy themselves. For example skin cell can make many more skin cells to repair damage to skin. But it can’t make any other type of cells found in body. But Hematopoietic Stem Cells can mature into different types of blood cells found in the body. During preparation for labor there occurs a maternal – fetal transfer of cells which boosts the immune systems of both the mother and baby.
So cord blood, at the time of delivery, becomes a rich source of stem cells and other cells of the immune system. Cord blood can be easily collected at the time of baby’s birth via the umbilical cord. It causes no harm to the mother or baby. Cord blood has an abundance of stem cells and immune system cells. Banked cord blood is most abundant in white blood cells and stem cells. Hematopoietic stem cells are also found in blood and bone marrow in adults and children.
What is Cord Blood Banking?
Cord blood banking is the process of collecting the cord blood at the time of delivery. Thereafter the cord blood is processed. Red blood cells are minimized. Stem cells and other cells are extracted during this process and cryogenically frozen for long term preservation. These frozen cells represent the immune system and have potential future medical use. So cord blood banking is a term used for storing various types of cells extracted from cord blood. It can also be termed Stem Cell Banking.
How is blood collected?
Collecting umbilical cord blood is a simple process. You don’t have to worry about the details of collecting, processing and cryogenic preservation of your baby’s cord blood at the time of delivery. Following are the steps in cord blood banking you should be aware of:
-
You need to the Cord Blood Bank in advance. If the delivery is taking place in a clinic or a hospital, they can take care of this process. Ask them about the details.
-
The cord blood bank will send a collection kit. Kits are normally stored at room temperature. Some kits are required to be stored at lower temperature. Take the kit along with the expectant mother, to the delivery hospital.
-
The expecting mother’s blood may be tested for any infectious diseases etc.
-
Upon birth but before the placenta is delivered, the doctor/nurse will clamp and cut the umbilical cord as normal.
-
Some cord blood still remains in the umbilical cord and placenta. There is still 40 to 120 CC of cord blood remaining. The doctor/nurse will extract this cord blood from the umbilical cord. There is no risk or harm to either the baby or the mother. This procedure is painless and risk-free.
-
The collection bag with the baby’s cord blood are placed back inside the collection kit and taken to blood bank for further processing and storing.

How does it work?
Before selecting a cord blood bank you should check its accreditation. AABB accreditation is world’s gold standard in private cord blood banking. It guarantees that your baby's cord blood has been screened, processed and stored according to the International Quality Assurance Programme, preferred by Transplant Surgeons.
Our body's immune system is designed to automatically find and destroy what it believes to be outside contaminants. Stem cells and other cells of a person’s immune system cannot be transfused into just anyone. The stem cells being transfused must match the cells of the patient either completely or to a certain degree. This degree of match depends on what type of decease is being treated. But cord blood taken from a baby's umbilical cord, at the time of delivery, is always a perfect match for the baby. It may match even immediate family members. Cord blood can be donated to a Public Bank or Family Bank.
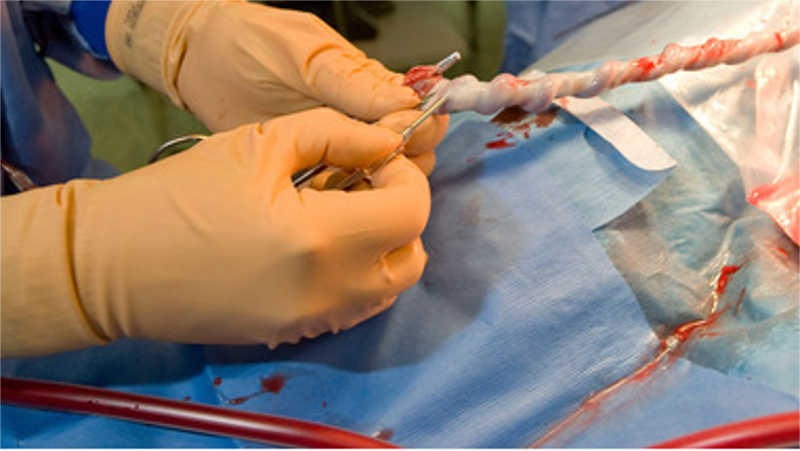
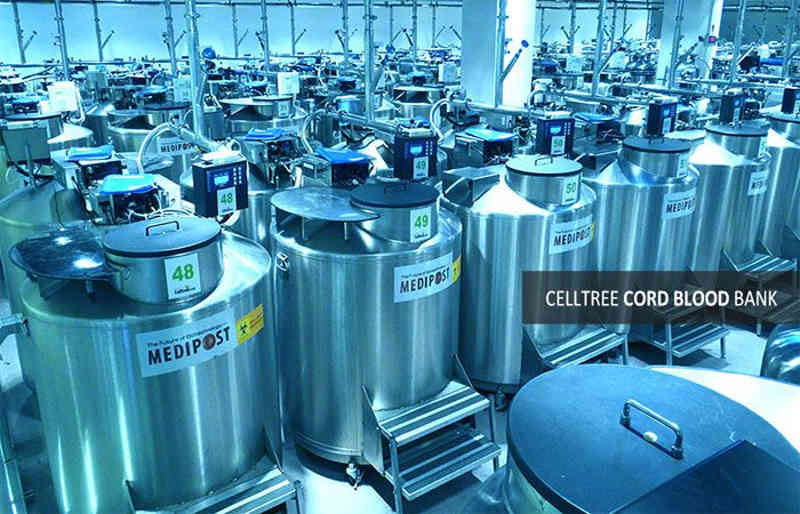
Processing and Cryopreservation
When the cord blood arrives at cord blood bank it is immediately processed to maintain viability of the stem cells and immune system cells found in the cord blood. Following is an outline of activities at the blood bank:
-
A sample of the cord blood is tested for microbiological contamination. The mother’s blood is also tested for infectious diseases.
-
As the activity mentioned above is being done, the cord blood is processed to drastically reduce the number of red blood cells. Its total volume also reduces. The stem cells and immune system cells are isolated.
-
The processing method is very important and affects the purity of the final product. Red blood cells must be reduced to the minimum as it can have a negative impact on a cord blood transfusion. There is a certain number of stem cells that must be present. Then only the cord blood will be effective in disease treatment in future. So the processing method must have the ability to reduce the number of RBCs and capture more stem cells.
-
The stem cells and immune system cells are isolated and extracted from the plasma and red blood cell. Then they are mixed with a cryogenic protectant and stored in a cryo-bag.
-
This cryo-bag is housed in a protective metal cassette and placed in vapor-phase liquid nitrogen freezer for long-term preservation.
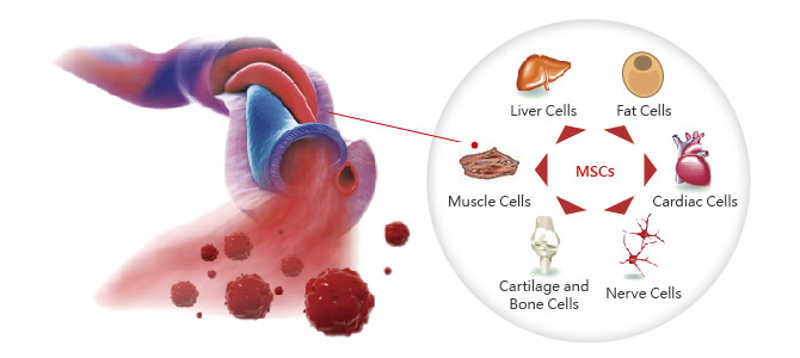
What diseases can be treated by cord blood?
When you save cord blood in a family bank, you have an option that the baby can use its own stem cells for an autologous treatment. Even an immediate relative (sibling or parents) can use the stem cells for an allogeneic treatment. Following are some of the diseases for which transplants of blood-forming stem cells are a standard treatment. The stem cells may be extracted from bone marrow, peripheral blood, or cord blood.
-
Leukemia (cancer of the blood immune system).
-
Melodysplastic Syndromes (pre leukemia)
-
Lymphoma
-
Anemias
-
Disorder of immune system
-
Inherited metabolic disorder
-
Neurologic disorder
-
Auto immune disorder
-
Cardiovascular
-
Diabitic
-
Genetic and/or Metabolic Disorders
Conclusion
Cord blood is the blood taken at the time of delivery of baby that is left in the umbilical cord and placenta after birth. It contains special cells called hematopoietic stem cells. It can be used to treat some types of diseases.
Cord blood can be frozen and stored. It is much harder to collect bone marrow than to collect cord blood. Collecting bone marrow has certain risks and can be painful for the donor. Stem cells from cord blood are less likely to be rejected and can be used by relatives also. Cord blood is in use today in hospitals around the world. There are over 80 types of deceases that can be treated using stem cells extracted from cord blood. You can store the stem cells in Family Bank or Public Bank for future use.
Get Free IVF & Surrogacy Consultation
Top IVF Doctors




Dr. Prerna Gupta
MBBS, MD (Obs & Gyn), DNB, MNAMS, MRCOG, Commonwealth Fellow (Reproductive Medicine)